Cosine is even function cos(-x)=cos x
We prove here that the cosine function cos(-x)=cos x is even using the unit circle.
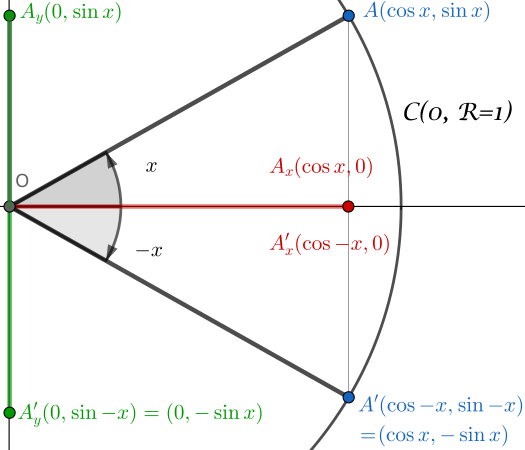
We start with the following configuration:
- unit circle $\mathcal{C}(O,R=1)$
- definition of the angle $x$
- definition of the angle $-x$
Now consider the triangles: $(OA_xA)$ and $(OA’_xA’)$.
Proof that cosine is an even function cos(-x) = cos (x)
Take the definition of the cosines of the angles $x$ and $-x$.
In the triangle $(OA_xA)$ :
\[\cos x=\frac{\textrm{adjacent}}{\textrm{hypotenuse}}=\frac{|OA_x|}{R}=\frac{|OA_x|}{1}=|OA_x|\]In the triangle $(OA’_xA’)$:
\[\cos (-x)=\frac{\textrm{adjacent}}{\textrm{hypotenuse}}=\frac{|OA'_x|}{R}=\frac{|OA'_x|}{1}=|OA'_x|\]By construction: $\vert OA_x\vert = \vert OA’_x\vert $, then we have
\[\forall x\in \mathbb{R},\quad: \cos (-x)=\cos x\]If you found this post or this website helpful and would like to support our work, please consider making a donation. Thank you!
Help UsArticles in the same category
- Trigonometry addition formula sinh(x + y) = sinh x cosh y +cosh x sinh y
- Trigonometry addition formula sinh(x - y) = sinh x cosh y - cosh x sinh y 8080624
- Trigonometry addition formula sin(a-b)=sin a cos b - sin b cos a
- Trigonometry addition formula sin(a+b)=sin a cos b + cos a sin b
- Trigonometry addition formula cosh(x + y) = cosh x cosh y +sinh x sinh y
- Trigonometry addition formula cosh(x - y) = cosh x cosh y - sinh x sinh y 8080622
- Trigonometry addition formula cos(a+b)=cos a cos b - sin a sin b
- Trigonometry addition formula cos(a-b)=cos a cos b + sin a sin b 8080598
- Trigonometric formula sin(2x)=2 sin x cos x
- Tangent is an odd function tan(-x)=-tan x
- Sine is an odd function sin(-x)=-sin x
- Demonstration / proof of cos²x + sin²x=1
- Cosine is even function cos(-x)=cos x
- Mathematics - Trigonometry